Antennas And Feed Lines
Antenna Length and Frequencies
T61B02
Which
component is used to radiate radio energy?
A.
An antenna
B.
An earth ground
C.
A chassis ground
D.
A potentiometer
T94A01
How
do you calculate the length (in feet) of a half-wavelength dipole antenna?
A.
Divide 150 by the antenna's operating frequency (in MHz) [150/f(in MHz)]
B.
Divide 234 by the antenna's operating frequency (in MHz) [234/f (in MHz)]
C.
Divide 300 by the antenna's operating frequency (in MHz) [300/f (in MHz)]
D.
Divide 468 by the antenna's operating frequency (in MHz) [468/f (in MHz)]
T92A02
How
do you calculate the length (in feet) of a quarter-wavelength vertical antenna?
A.
Divide 150 by the antenna's operating frequency (in MHz) [150/f (in MHz)]
B.
Divide 234 by the antenna's operating frequency (in MHz) [234/f (in MHz)]
C.
Divide 300 by the antenna's operating frequency (in MHz) [300/f (in MHz)]
D.
Divide 468 by the antenna's operating frequency (in MHz) [468/f (in MHz)]
T93A03
How
long should you make a quarter-wavelength vertical antenna for 440 MHz
(measured to the nearest inch)?
A.
12 inches
B.
9 inches
C.
6 inches
D.
3 inches
T91A04
How
long should you make a quarter-wavelength vertical antenna for 28.450 MHz
(measured to the nearest foot)?
A.
8 ft
B.
12 ft
C.
16 ft
D.
24 ft
T93A05
How
long should you make a quarter-wavelength vertical antenna for 146 MHz
(measured to the nearest inch)?
A.
112 inches
B.
50 inches
C.
19 inches
D.
12 inches
T91A06
If
an antenna is made longer, what happens to its resonant frequency?
A.
It decreases
B.
It increases
C.
It stays the same
D.
It disappears
T91A08
How
could you decrease the resonant frequency of a dipole antenna?
A.
Lengthen the antenna
B.
Shorten the antenna
C.
Use less feed line
D.
Use a smaller size feed line
T92A07
If
an antenna is made shorter, what happens to its resonant frequency?
A.
It decreases
B.
It increases
C.
It stays the same
D.
It disappears
T92A09
How
could you increase the resonant frequency of a dipole antenna?
A.
Lengthen the antenna
B.
Shorten the antenna
C.
Use more feed line
D.
Use a larger size feed line
Non-Directional Antennas
T94B07
What
type of non-directional antenna is easy to make at home and works well
outdoors?
A.
A Yagi
B.
A delta loop
C.
A cubical quad
D.
A ground plane
Directional Antennas
T93B01
What
is a directional antenna?
A.
An antenna that sends and receives radio energy equally well in all directions
B.
An antenna that cannot send and receive radio energy by skywave or skip
propagation
C.
An antenna that sends and receives radio energy mainly in one direction
D.
An antenna that uses a directional coupler to measure power transmitted
T23D09
Which
type of antenna would be a good choice as part of a portable HF amateur station
that could be set up in case of an emergency?
A.
A three-element quad
B.
A three-element Yagi
C.
A dipole
D.
A parabolic dish
T91B02
How
is a Yagi antenna constructed?
A.
Two or more straight, parallel elements are fixed in line with each other
B.
Two or more square or circular loops are fixed in line with each other
C.
Two or more square or circular loops are stacked inside each other
D.
A straight element is fixed in the center of three or more elements that angle
toward the ground
T92B03
How
many directly driven elements do most parasitic beam antennas have?
A.
None
B.
One
C.
Two
D.
Three
T91B04
What
is a parasitic beam antenna?
A.
An antenna in which some elements obtain their radio energy by induction or
radiation from a driven element
B.
An antenna in which wave traps are used to magnetically couple the elements
C.
An antenna in which all elements are driven by direct connection to the feed
line
D.
An antenna in which the driven element obtains its radio energy by induction or
radiation from director elements
T94B05
What
are the parasitic elements of a Yagi antenna?
A.
The driven element and any reflectors
B.
The director and the driven element
C.
Only the reflectors (if any)
D.
Any directors or any reflectors
T92B06
What
is a cubical quad antenna?
A.
Four straight, parallel elements in line with each other, each approximately
1/2-electrical wavelength long
B.
Two or more parallel four-sided wire loops, each approximately one-electrical
wavelength long
C.
A vertical conductor 1/4-electrical wavelength high, fed at the bottom
D.
A center-fed wire 1/2-electrical wavelength long
Multiband
Antennas
T91A10
What
is one advantage to using a multiband antenna?
A.
You can operate on several bands with a single feed line
B.
Multiband antennas always have high gain
C.
You can transmit on several frequencies simultaneously
D.
Multiband antennas offer poor harmonic suppression
T94A11
What
is one disadvantage to using a multiband antenna?
A.
It must always be used with a balun
B.
It will always have low gain
C.
It cannot handle high power
D.
It can radiate unwanted harmonics
T74B11
What
would you use to connect a dual-band antenna to a mobile transceiver which has
separate VHF and UHF outputs?
A.
A dual-needle SWR meter
B.
A full-duplex phone patch
C.
Twin high-pass filters
D.
A duplexer
Antenna
Polarization
T94B08
What
electromagnetic-wave polarization does most man-made electrical noise have in
the HF and VHF spectrum?
A.
Horizontal
B.
Left-hand circular
C.
Right-hand circular
D.
Vertical
Connecting the
Antenna to the Transceiver
T74A02
What
connects your transceiver to your antenna?
A.
A dummy load
B.
A ground wire
C.
The power cord
D.
A feed line
T72A01
What
would you connect to your transceiver if you wanted to switch it between
several antennas?
A.
A terminal-node switch
B.
An antenna switch
C.
A telegraph key switch
D.
A high-pass filter
Coaxial Cable
T92B11
Why
does coaxial cable make a good antenna feed line?
A.
You can make it at home, and its impedance matches most amateur antennas
B.
It is weatherproof, and it can be used near metal objects
C.
It is weatherproof, and its impedance is higher than that of most amateur
antennas
D.
It can be used near metal objects, and its impedance is higher than that of
most amateur antennas
Balun
T91B10
Where
would you install a balun to feed a dipole antenna with 50-ohm coaxial cable?
A.
Between the coaxial cable and the antenna
B.
Between the transmitter and the coaxial cable
C.
Between the antenna and the ground
D.
Between the coaxial cable and the ground
Standing Wave
Ratio
T94B09
What
does standing-wave ratio mean?
A.
The ratio of maximum to minimum inductances on a feed line
B.
The ratio of maximum to minimum capacitances on a feed line
C.
The ratio of maximum to minimum impedances on a feed line
D.
The ratio of maximum to minimum voltages on a feed line
T44B09
What
instrument is used to measure the relative impedance match between an antenna
and its feed line?
A.
An ammeter
B.
An ohmmeter
C.
A voltmeter
D.
An SWR meter
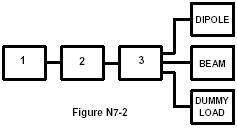
T73A07
In
Figure N7-2, if block 1 is a transceiver and block 3 is an antenna switch, what
is block 2?
A.
A terminal-node switch
B.
A dipole antenna
C.
An SWR meter
D.
A high-pass filter
T41B06
What
does a very high SWR reading mean?
A.
The antenna is the wrong length, or there may be an open or shorted connection
somewhere in the feed line
B.
The signals coming from the antenna are unusually strong, which means very good
radio conditions
C.
The transmitter is putting out more power than normal, showing that it is about
to go bad
D.
There is a large amount of solar radiation, which means very poor radio
conditions
T42B11
What
does an SWR reading of 1:1 mean?
A.
An antenna for another frequency band is probably connected
B.
The best impedance match has been attained
C.
No power is going to the antenna
D.
The SWR meter is broken
T43B05
What
does an SWR reading of less than 1.5:1 mean?
A.
An impedance match that is too low
B.
An impedance mismatch; something may be wrong with the antenna system
C.
A fairly good impedance match
D.
An antenna gain of 1.5
T42B07
If
an SWR reading at the low frequency end of an amateur band is 2.5:1, increasing
to 5:1 at the high frequency end of the same band, what does this tell you
about your 1/2-wavelength dipole antenna?
A.
The antenna is broadbanded
B.
The antenna is too long for operation on the band
C.
The antenna is too short for operation on the band
D.
The antenna is just right for operation on the band
T43B08
If
an SWR reading at the low frequency end of an amateur band is 5:1, decreasing
to 2.5:1 at the high frequency end of the same band, what does this tell you
about your 1/2-wavelength dipole antenna?
A.
The antenna is broadbanded
B.
The antenna is too long for operation on the band
C.
The antenna is too short for operation on the band
D.
The antenna is just right for operation on the band
T43B10
If
you use an SWR meter designed to operate on 3-30 MHz for VHF measurements, how
accurate will its readings be?
A.
They will not be accurate
B.
They will be accurate enough to get by
C.
If it properly calibrates to full scale in the set position, they may be
accurate
D.
They will be accurate providing the readings are multiplied by 4.5
Antenna Tuners
T71A04
What
does an antenna tuner do?
A.
It matches a transceiver output impedance to the antenna system impedance
B.
It helps a receiver automatically tune in stations that are far away
C.
It switches an antenna system to a transceiver when sending, and to a receiver
when listening
D.
It switches a transceiver between different kinds of antennas connected to one
feed line
T72A08
In
Figure N7-3, if block 1 is a transceiver and block 2 is an SWR meter, what is
block 3?
A.
An antenna switch
B.
An antenna tuner
C.
A key-click filter
D.
A terminal-node controller
Wattmeters
T41C08
What
does a directional wattmeter measure?
A.
Forward and reflected power
B.
The directional pattern of an antenna
C.
The energy used by a transmitter
D.
Thermal heating in a load resistor
T41C10
Why
might you use a peak-reading RF wattmeter at your station?
A.
To make sure your transmitter's output power is not higher than that authorized
by your license class
B.
To make sure your transmitter is not drawing too much power from the AC line
C.
To make sure all your transmitter's power is being radiated by your antenna
D.
To measure transmitter input and output power at the same time
T41C03
Where
should an RF wattmeter be connected for the most accurate readings of
transmitter output power?
A.
At the transmitter output connector
B.
At the antenna feed point
C.
One-half wavelength from the transmitter output
D.
One-half wavelength from the antenna feed point
T42C07
At
what line impedance do most RF watt meters usually operate?
A.
25 ohms
B.
50 ohms
C.
100 ohms
D.
300 ohms
T42C09
If
a directional RF wattmeter reads 90 watts forward power and 10 watts reflected
power, what is the actual transmitter output power?
A.
10 watts
B.
80 watts
C.
90 watts
D.
100 watts
Dummy Antennas
T42A08
What
device is used in place of an antenna during transmitter tests so that no
signal is radiated?
A.
An antenna matcher
B.
A dummy antenna
C.
A low-pass filter
D.
A decoupling resistor
T41A09
Why
would you use a dummy antenna?
A.
For off-the-air transmitter testing
B.
To reduce output power
C.
To give comparative signal reports
D.
To allow antenna tuning without causing interference
T22A04
How
can on-the-air interference be minimized during a lengthy transmitter testing
or loading-up procedure?
A.
Choose an unoccupied frequency
B.
Use a dummy load
C.
Use a non-resonant antenna
D.
Use a resonant antenna that requires no loading-up procedure
T72A05
In
Figure N7-1, if block 1 is a transceiver and block 3 is a dummy antenna, what
is block 2?
A.
A terminal-node switch
B.
An antenna switch
C.
A telegraph key switch
D.
A high-pass filter
T74A06
In
Figure N7-1, if block 1 is a transceiver and block 2 is an antenna switch, what
is block 3?
A.
A terminal-node switch
B.
An SWR meter
C.
A telegraph key switch
D.
A dummy antenna
T41A10
What
minimum rating should a dummy antenna have for use with a 100 watt single-sideband
phone transmitter?
A.
100 watts continuous
B.
141 watts continuous
C.
175 watts continuous
D.
200 watts continuous
T42A11
Would
a 100 watt light bulb make a good dummy load for tuning a transceiver?
A.
Yes; a light bulb behaves exactly like a dummy load
B.
No; the impedance of the light bulb changes as the filament gets hot
C.
No; the light bulb would act like an open circuit
D.
No; the light bulb would act like a short circuit
Answer
Key
The
answer to each question is coded in the 3rd position of the question
number.
Example:
The answer to question T42A11 is B.
T42A11
^
|
|
1
= A
2
= B
3
= C
4
= D